

The same cross-linking assay in panel a was performed with cells expressing 3HA-Hrd3p with or without the P TDH3- hemi-HRD1 allele. (d) hemi-Hrd1p expression inhibited Hrd3p cross-linking Hrd1p. Precipitated proteins were immunoblotted with an anti-HA mAb to detect coimmunoprecipitated 3HA-Hrd3p (top), or with an anti-GFP mAb to detect immunoprecipitated Hrd1p-GFP fusions (bottom). Cells coexpressing 3HA-Hrd3p and the indicated Hrd1p-GFP fusion were subject to the cross-linking assay using anti-GFP antisera to immunoprecipitate the Hrd1p-GFP fusions from the lysates. (c) Hrd3p cross-linked to hemi-Hrd1p-GFP, but not RING-Hrd1p-GFP. Bottom row, cartoon representations of the various Hrd1p constructs including wt-Hrd1p, only the Hrd1p transmembrane domain (hemi-Hrd1p), and only the COOH-terminal RING-H2 domain (termed RING-Hrd1p). The start and end of each domain are indicated by the number of the corresponding amino acid residue below. Top row, linear representation of Hrd1p domains. Precipitated proteins were next immunoblotted with an anti-HA mAb to detect coimmunoprecipitated 3HA-Hrd3p (top) or with an anti-Hrd1p polyclonal antisera to verify equal amounts of immunoprecipitated Hrd1p (bottom).

Log phase cells expressing the indicated 3HA epitope–tagged proteins were treated with the indicated concentrations of DSP, lysed, and immunoprecipitated with anti-Hrd1p antisera. Hrd1p and Hrd3p interacted via the Hrd1p NH 2-terminal transmembrane domain. The HRD complex engages in lumen to cytosol communication required for regulation of Hrd1p stability and the coordination of ERAD events on both sides of the ER membrane. Our studies show that Hrd1p and Hrd3p form a stoichiometric complex with ERAD determinants in both the lumen and the cytosol. Additionally, we identified a lumenal region of Hrd3p dispensable for regulation of Hrd1p stability, but absolutely required for normal ERAD. An engineered, completely lumenal, truncated version of Hrd3p functioned normally in both ERAD and Hrd1p stabilization, indicating that the lumenal domain of Hrd3p regulates the cytosolic Hrd1p RING-H2 domain by signaling through the Hrd1p transmembrane domain. Rigorous reevaluation of Hrd1p topology demonstrated that the Hrd1p RING-H2 domain is located and functions in the cytosol. We show that these two proteins directly interact through the Hrd1p transmembrane domain, allowing Hrd1p stability by Hrd3p-dependent control of the Hrd1p RING-H2 domain activity. The ER resident membrane proteins Hrd1p and Hrd3p play central roles in ERAD. ERAD occurs by processes on both sides of the ER membrane, including lumenal substrate scanning and cytosolic destruction by the proteasome.
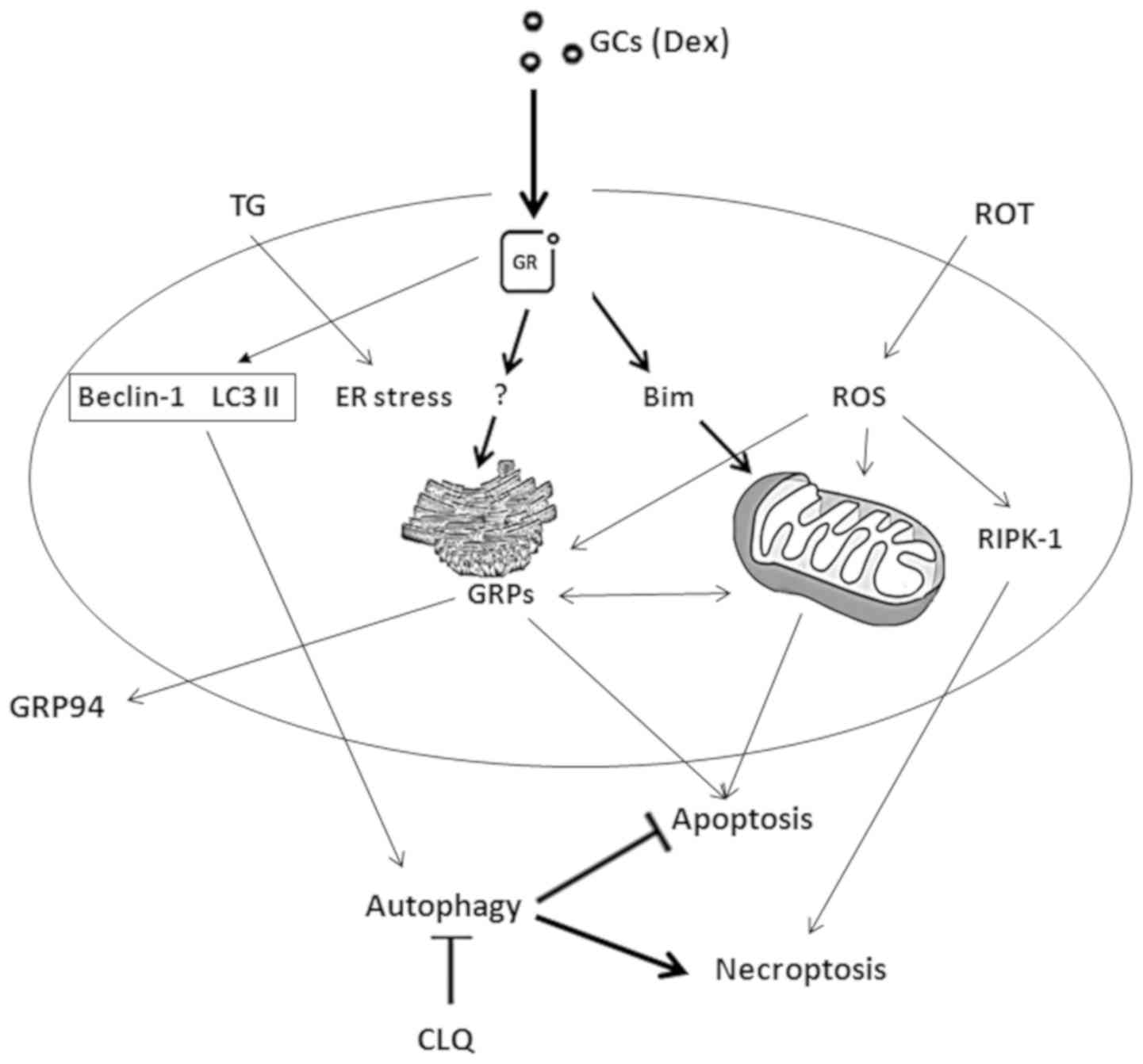
Therefore, redox and calcium homeostasis and protein glycosylation in the ER provide novel drug-targets for medical treatment in a wide array of diseases.Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation (ERAD) is required for ubiquitin-mediated destruction of numerous proteins. The unique set of enzymes, selection of metabolites, and characteristic ion and redox milieu of the luminal compartment strongly argue against the general permeability of the ER membrane.Īlterations in the luminal environment can trigger the unfolded protein response, a common event in a variety of pathological conditions. Mounting evidence supports the existence of a real barrier between the ER lumen and the cytosol. Ca(2+)-dependence of certain ER chaperones is a subject of intensive research. Transport of the required intermediates across the ER membrane and maintenance of the luminal redox conditions and Ca(2+) ion concentration are indispensable for appropriate protein maturation.Ĭooperation of enzymes and transporters to maintain a thiol-oxidizing milieu in the ER lumen has been recently elucidated. Compartmentation plays a crucial role in the post-translational modifications, such as oxidative folding and N-glycosylation in the ER lumen. Proteins destined to secretion and exposure on the cell surface are synthesized and processed in the extracellular-like environment of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of higher eukaryotic cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
